The cybersecurity industry is at a critical juncture as the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) in both defensive and offensive cyber strategies becomes more prevalent.
AI presents both opportunities and challenges for cybersecurity. On one hand, it enhances threat detection and response capabilities, enabling organizations to better protect their assets. On the other hand, cyber attackers are increasingly using AI, particularly large language models (LLMs) trained on malware, to conduct more targeted and effective attacks. As a result, cybersecurity vendors and users are bracing for a turbulent period over the next two to three years as they adapt to this new reality.
As companies grapple with the implications of AI on their security frameworks, cybersecurity budgets are set to expand considerably. According to PwC's 2024 Global Digital Trust Insights report, cybersecurity investments will constitute 14% of the total IT operational technology and automation budget in 2024, up from 11% in 2023. This uptick reflects the urgent need to defend against increasingly sophisticated cyber threats.
The cybersecurity market: industry insight and forecast by GlobalData.
Market size and growth forecasts
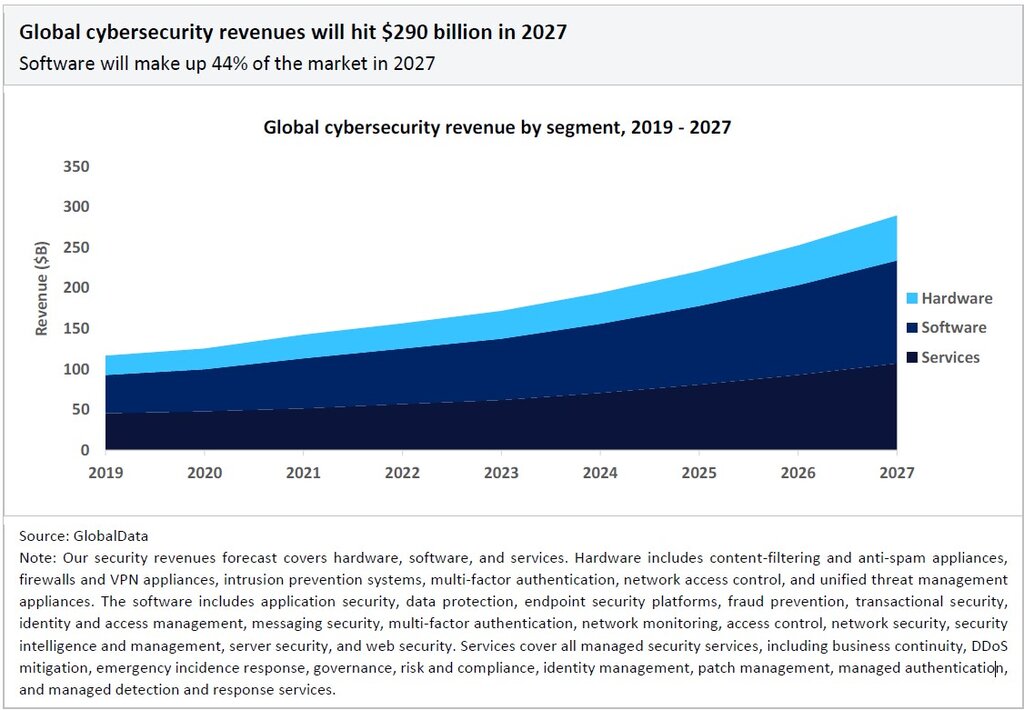
GlobalData forecasts that the cybersecurity market will reach $290 billion by 2027, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 13% between 2022 and 2027. Software-based cybersecurity products will be the largest market segment, contributing 44% of total revenue in 2027, with services accounting for 37%.
Managed security services – those outsourced to an external vendor or supplier – will be the largest single sub-segment within the cybersecurity market in 2027, as cybersecurity skill gaps drive a trend towards outsourcing security services. Revenues will increase by a CAGR of 13.5% between 2022 and 2027, reaching $107 billion in 2027.
The next largest segment is identity and access management (IAM) products, which are used to restrict end users from unauthorized access and monitor their behavior in a network. Revenues will rise by a CAGR of 13.7% between 2022 and 2027, reaching $28.9 billion in 2027.
IAM is one of the most important preventative security measures because of the rise in cloud computing and the increase in distributed workforces. According to Verizon’s 2023 Data Breach Investigations Report, 74% of all breaches include the human element, with people involved either via error, privilege misuse, use of stolen credentials, or social engineering.
M&A and investment trends in cybersecurity
The cybersecurity sector remains a focal point for mergers and acquisitions (M&A), driven by the relentless need for security companies to enhance their offerings amid constant cyber threats. This urgency is fueled by attacks on corporate clients, critical national infrastructure, and the security vendors themselves.
The sector saw robust M&A activity with 422 deals in 2021, a slight dip to 371 deals in 2022, and a rebound to 445 deals in 2023. Cisco’s $28 billion acquisition of Splunk marks a pivotal moment for AI-driven cybersecurity M&A. This deal is expected to catalyze further consolidation in the industry as larger companies seek to acquire startups and emerging firms to bolster their AI capabilities.
Key acquisitions in 2023 also highlighted a focus on cloud security, network security, and identity management, with CrowdStrike, HPE, and Delinea making significant moves. Looking ahead, the M&A focus is expected to shift towards companies with AI capabilities, reflecting the growing importance of AI in cybersecurity solutions.
Private equity firms are playing a dominant role in the cybersecurity landscape. Thoma Bravo's $2.3 billion acquisition of ForgeRock in August 2023 exemplifies this trend, despite facing scrutiny from the US Justice Department over competition concerns in identity access management. Thoma Bravo's cybersecurity portfolio, valued at approximately $45 billion as of December 2023, underscores the significant investments private equity firms are making in this sector. Other prominent investors include Insight Partners, TA Associates, Francisco Partners, and Advent International.
The surge in M&A activity will likely attract the attention of regulators, especially as a few private equity players continue to dominate the cybersecurity market. Ensuring competition and innovation within the industry will be critical as these acquisitions proceed.
Venture financing, essential for the growth of new cybersecurity firms, saw a decline in 2023. There were 431 venture capital (VC) deals, down from 680 in 2022 and 708 in 2021, per GlobalData. Despite the drop, notable successes like Splunk, founded in 2003 and backed by venture firms, highlight the critical role of VC in nurturing cybersecurity innovations. In 2023, there were 431 venture capital (VC) deals involving cybersecurity companies, a considerable fall from 2022, when there were 680 VC deals, and an even bigger decline from 2021, when there were 708 VC deals, according to GlobalData.
Key players in the cybersecurity landscape
Cybersecurity providers offer a range of products and services to secure client systems, from chip-based security and identity management to managed security services and risk compliance.
The cybersecurity ecosystem comprises various players specializing in different areas. Notable leaders and challengers across pivotal areas include:
- In Identity Management, leaders like Okta, Thales, and Microsoft, with challengers such as Duo Security and Ping Identity.
- In Network Security: leaders such as Fortinet and Palo Alto Networks, with challengers like Appgate and IBM.
- In Cloud Security, leaders including Microsoft and Zscaler, with challengers like IBM and Skyhigh Security.
Geopolitical factors impacting the cybersecurity space
Geopolitical tensions are significantly shaping the cybersecurity landscape, with ongoing conflicts in regions like Ukraine and the Middle East providing fertile ground for cyber attackers. State-sponsored actors and independent groups are leveraging these instabilities to launch sophisticated cyberattacks, particularly targeting critical infrastructure such as power grids and communication networks. These attacks have caused widespread disruptions, underscoring the need for robust cybersecurity measures.
In 2024, national elections in at least 64 countries, including the United States, the United Kingdom, Russia, and India, present significant opportunities for cyber attackers to influence outcomes and create discord. Cyber threats during these periods range from disinformation campaigns to direct attacks on election infrastructure, undermining electoral integrity and public trust in democratic institutions. This heightened risk necessitates comprehensive security protocols to protect electoral systems.
Nation-state actors increasingly use cyber operations for geopolitical objectives, extending beyond espionage to sabotage, intellectual property theft, and public opinion manipulation. These sophisticated operations require a coordinated response from national governments and the private sector to effectively defend against the complex and multifaceted nature of cyber threats.
GlobalData, the leading provider of industry intelligence, provided the underlying data, research, and analysis used to produce this article.
GlobalData’s Thematic Intelligence uses proprietary data, research, and analysis to provide a forward-looking perspective on the key themes that will shape the future of the world’s largest industries and the organisations within them.
